Arthritis is a term used to describe any condition that causes pain and inflammation in the joints.
ARTHRITIS
Introduction
Arthritis is a term used to describe any condition that causes pain and inflammation in the joints. It affects more than 50 million adults in the United States alone, making it the most common cause of disability in the country. Arthritis can be either inflammatory, such as rheumatoid arthritis, or non-inflammatory, such as osteoarthritis. Symptoms of arthritis vary depending on the type of arthritis, but can include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion.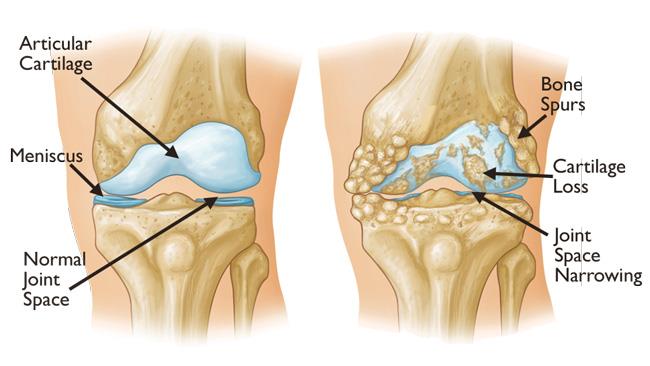
Causes of Arthritis
The exact causes of arthritis are not fully understood, but research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors can increase the risk of developing the condition. Some of the possible causes of arthritis include:
- Genetics: Some types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis have been linked to genetic factors.
- Age: As people age, the risk of developing arthritis increases.
- Obesity: Being obese or overweight can increase the risk of developing certain types of arthritis.
- Injury: Injury to a joint can increase the risk of developing arthritis in that joint.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing certain types of arthritis.
- Infection: Infections, such as Lyme disease, can increase the risk of developing certain types of arthritis.
Symptoms of Arthritis
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type of arthritis, but some of the most common symptoms include:
- Joint pain: Pain in the joints is the most common symptom of arthritis.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the joints is another common symptom of arthritis.
- Swelling: Swelling in the joints is another symptom of arthritis.
- Decreased range of motion: Arthritis can cause a decrease in range of motion in the affected joints.
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common symptom of arthritis.
Diagnosing Arthritis
The diagnosis of arthritis is made through a clinical evaluation of the patient's medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. It is important to note that different types of arthritis can have similar symptoms, so an accurate diagnosis is essential for proper treatment.
Types of Arthritis
Arthritis is a term used to describe inflammation of the joints. There are over 100 different types of arthritis, but some of the most common include:
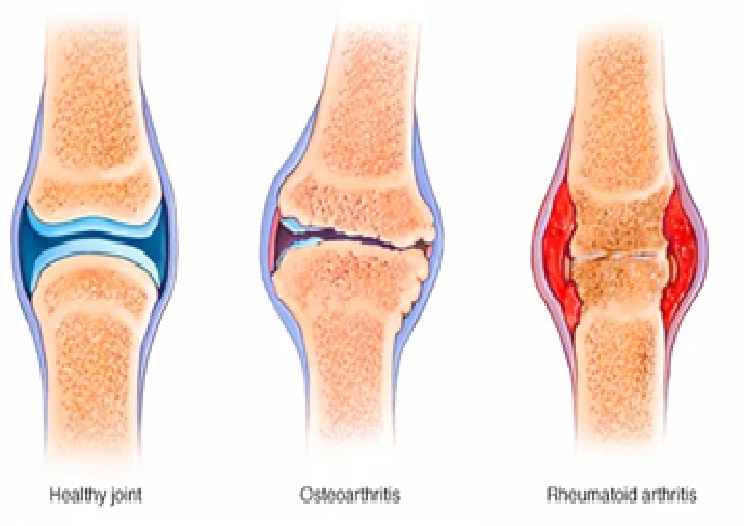
- Osteoarthritis - a degenerative condition caused by the wear and tear of joints
- Rheumatoid arthritis - an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and damage to joints
- Psoriatic arthritis - a type of arthritis that occurs in people with psoriasis
- Gout - a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints
- Ankylosing spondylitis - a type of arthritis that primarily affects the spine
- Lupus arthritis - a type of arthritis that occurs in people with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Reactive arthritis - a type of arthritis that occurs after a bacterial infection
These are just a few examples of the types of arthritis.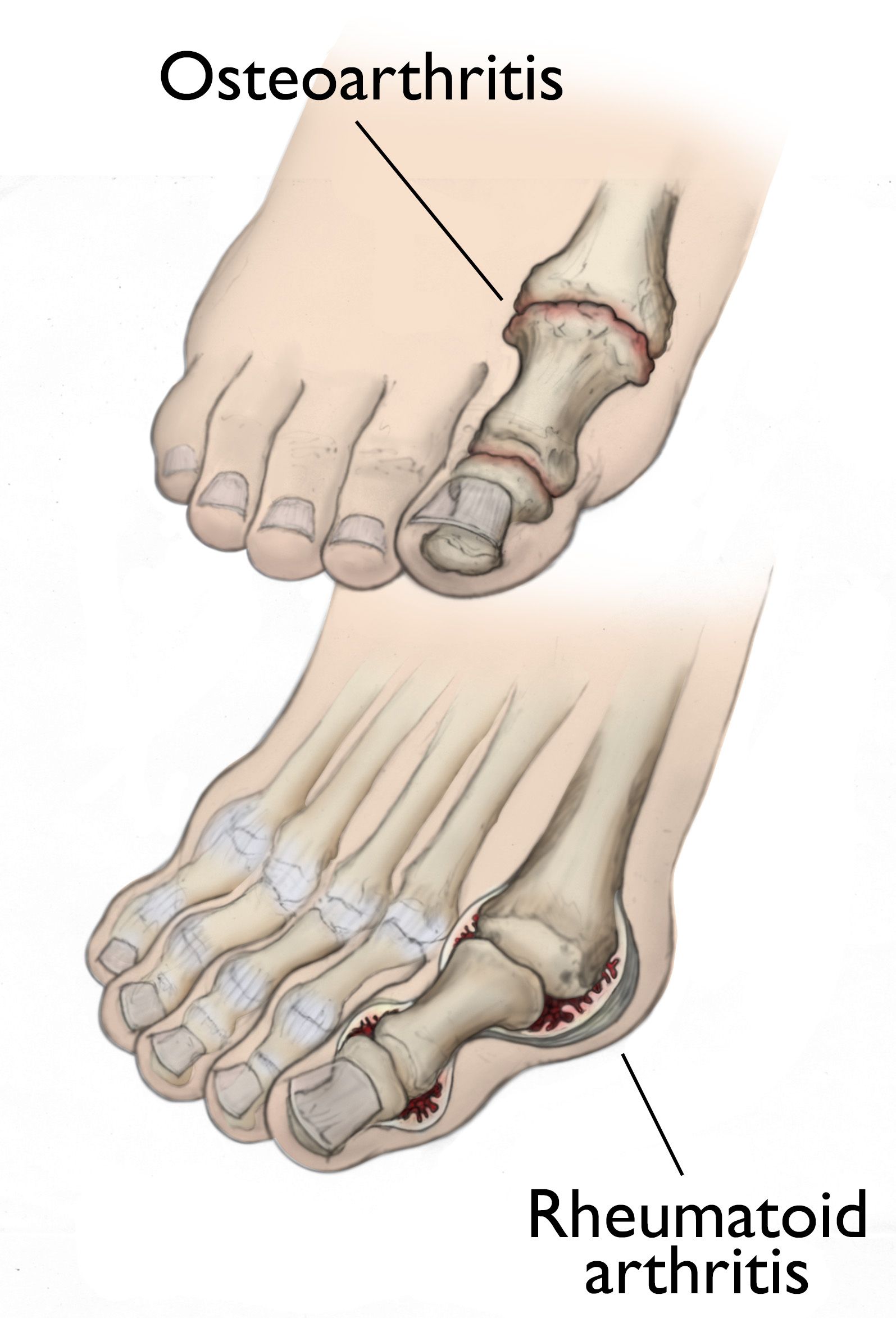
Treating Arthritis
When it comes to treating arthritis, there are several steps that can be taken to alleviate the symptoms and improve quality of life. First, resting the joint can help to reduce inflammation and pain. It is important to avoid activities that cause too much strain and stress on the joint, such as running or heavy lifting.
Secondly, medications can be prescribed by a doctor to reduce arthritis symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nsaids) are a type of over-the-counter pain relievers that can help reduce joint pain and stiffness. Other medications, such as corticosteroids, can also be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling.
Thirdly, physical therapy is key to reducing arthritis symptoms. Exercises that are tailored to the individual can help to reduce pain and strengthen muscles around the joints. A physiotherapist can create an exercise program that suits the individual's needs and abilities.
Finally, lifestyle changes can make a big difference in managing arthritis. Eating a balanced diet and maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce inflammation and strain on the joints. Stretching can also be beneficial in improving flexibility and joint range of motion.
In conclusion, there are several steps that can be taken to manage the symptoms of arthritis. Resting the joint, taking medications, physical therapy, and making lifestyle changes can all help to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Comments